Ladakh: Introduction
Ladakh area is endowed with natural attractions such as mountains and lakes with a strong influence of Buddhist religions. It is located in the northern region of the South Asian sub-region. The territorial issues have remained an area of concern in Ladakh especially involving India, Pakistan and China. There is a history that states that Ladakh acceded to Pakistan in 1947. To appreciate the current position of this region, we are going to discuss it in this article from a historical, political, and legal perspective.
History of Ladakh
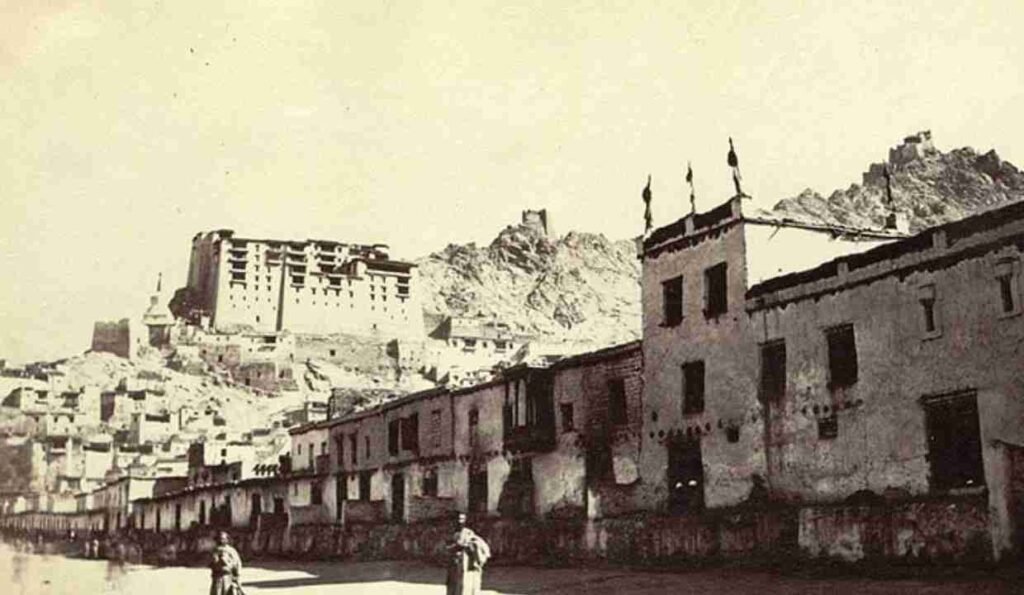

Ancient History
Looking at the history of Ladakh, it occupies a rather long strip of territory in the southeast of Kashmir. Historically it was a productive link between the Indian Ocean and the historic middle Asian corridor to Tibet. Ladakh had been an independent kingdom right from the Time of Bhitonda’s reign but was taken over by the Dogra rulers of Jammu in mid nineteenth century.
Modern History of Ladakh
In the middle of the 19th century, Ladakh was made part of the Dogra kingdom which formed later part of the large crown state of Jammu and Kashmir. Ladakh continued to be virtually out of the political actions of British India until the time of partition in 1947.
Geographical Location
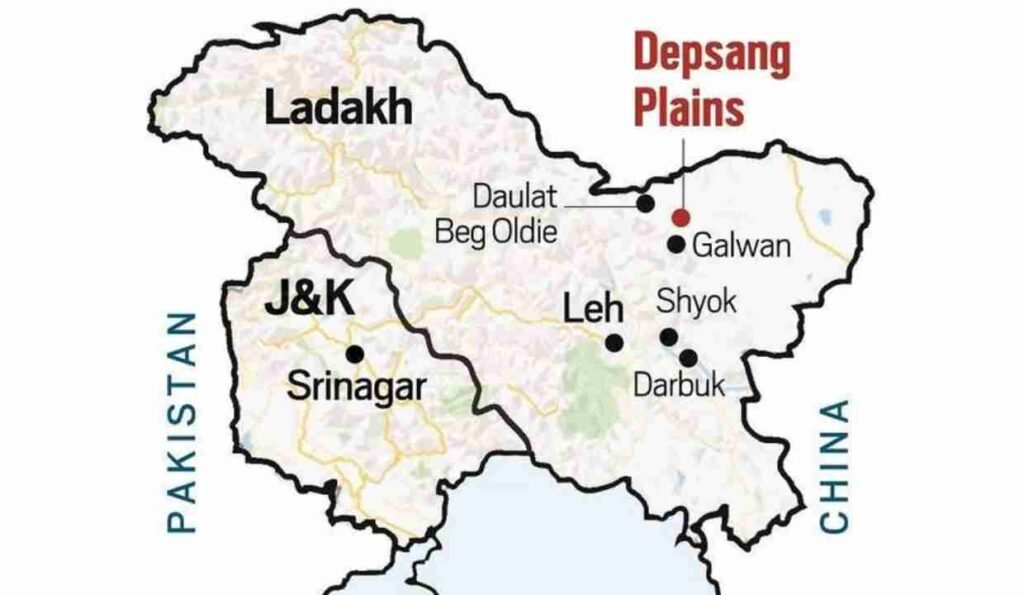
Ladakh’s Borders
Ladakh shares its boundary with Pakistan in the west, China in the north and Jammu and Kashmir in the south. It has thereby become a battlefield of the three nations as each lays claims to a part of the region.
Ladakh’s Harsh and Arid Climate: A High-Altitude Desert in the Himalayas
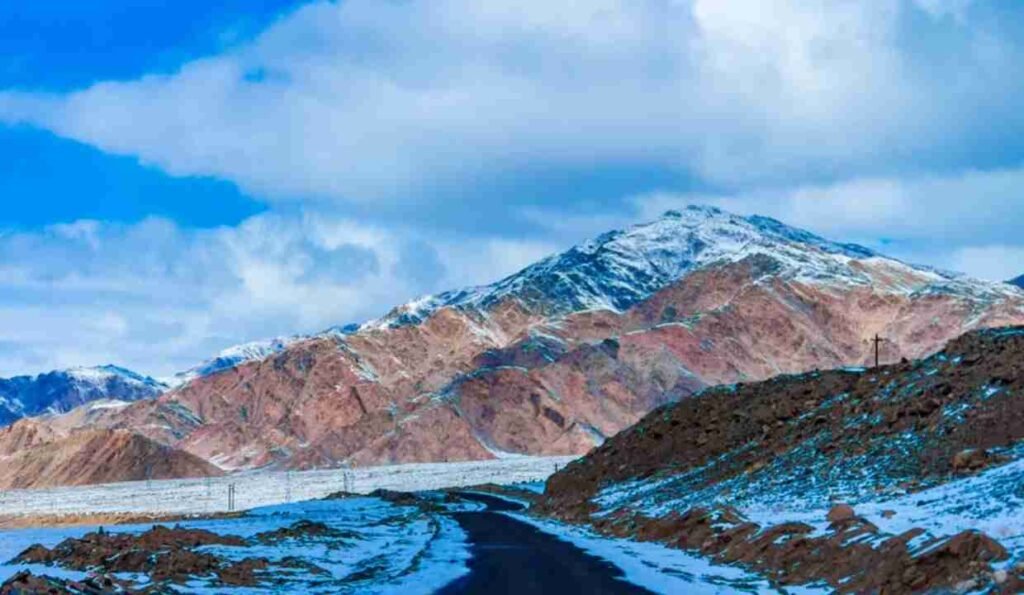

Extreme Temperatures, Minimal Rainfall, and Unique Seasonal Variations
Ladakh’s climate is cold and arid due to its high altitude and geographical location in the Himalayas. It experiences long, harsh winters with temperatures often dropping below freezing, especially at night, sometimes reaching as low as -30°C (-22°F) in the coldest months. Summers are short but relatively warm, with daytime temperatures ranging from 20°C to 30°C (68°F to 86°F), though nights remain cool. Rainfall is scarce, as the region lies in a rain shadow created by the Himalayas, receiving less than 100 mm of precipitation annually, mostly in the form of snow. The intense sunlight and dry air make Ladakh’s climate challenging but also contribute to its unique desert-like landscape.
Political Significance
Role of Ladakh in Regional Politics
Ladakh is preeminent in the politics of the region because its position lies on the doorstep of India, Pakistan as well as China. It became a source of conflict in the larger Kashmir context which emerged after the Partition of British India.
Key Territorial Disputes
The major decentralized territorial disputes on the issue of Ladakh involve Gilgit-Baltistan presently under the occupation of Pakistan and Aksai Chin occupied by China. Both these regions are located near Ladakh thus complicating the border issues.
Ladakh’s Status Post-1947
Partition of British India
Since the division of British India in 1947, the state of Jammu and Kashmir including Ladakh and Baltistan remained in a rather complicated position. Its ruler Maharaja Hari Singh decided to join India and this led to Military Hostilities between India and Pakistan.
UN Involvement in Kashmir Dispute
The question of Kashmir, including Ladakh, was soon referred to the United Nations where it was resolved that there should be a cease-fire and the people be allowed to decide for themselves through the Holding of a ‘Plebiscite’. However, this plebiscite was never conducted in that part of the state and therefore continues to remain a part of the Indian administration.
Pakistan’s Claim on Ladakh
1947 Events and Legal Basis
Pakistan argues that Ladakh like Kashmir should have been a part of Pakistan given its population of Muslims in some regions for instance in Gilgit Baltistan. In the broad context, Pakistan has always considered the region as its strategic territory which it has tried to occupy through political and operational conquest.
Pakistan’s Argument for Ladakh
Pakistan argues that while Ladakh formed part of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir and that there was a sizeable Muslim populace in this area, Ladakh should have joined Pakistan after the Partition in 1947.
International Recognition
Status of Ladakh Globally
As much as Pakistan likes to say otherwise most of the world, including the United Nations recognizes Ladakh as India. India continues to exercise sovereignty over Ladakh and runs the territory as a Union Territory, thus strengthening its position on the political status of the area.
Counterarguments: India’s Claim
India’s Legal Stand
According to India’s legal rights, Ladakh is a part of the Indian territory because Maharaja Hari Singh signed the Instrument of Accession wherein Jammu and Kashmir including Ladakh became a legal territory of the Indian Union.
Integration into the Indian Union
A very recent action by India was undertaking the center’s final- bold act in the entire episode in 2019- of issuing the communication that annulled Article 370 of the Constitution and carving out Jammu and Kashmir into two Union Territories, Jammu& Kashmir and Ladakh.
Role of China
China’s Influence on the Dispute
China also has a major stake in the Ladakh issue mainly because of its possession of Aksai Chin which is a region of Ladakh that has been under the administration of china since the 1962 Sino-Indian War.
Aksai Chin Controversy
Aksai Chin remains one of the most sensitive issues on sovereignty in the India- China relationship. Even though analytically one can distance Pakistan’s ambitions on Ladakh, having China involved intensifies the territorial issue.
Ladakh’s Cultural and Religious Identity
Tibetan Influence
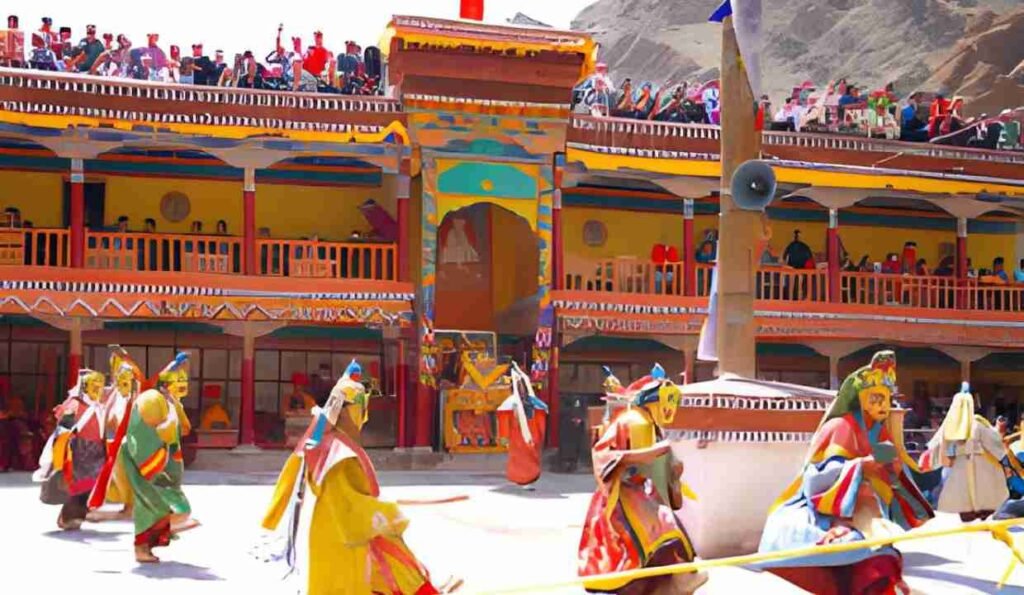

According to cultural orientation, Ladakh is more related to Tibet, especially by its predominant Buddhist religion. The main religion, which is practiced in the region remains to be Tibetan Buddhism.
Indigenous People and Traditions

Ladakh has its unique cultural profile with democracy based on Buddhism and Islam which again creates a conflict for a territory by both India and Pakistan.
Economic Importance of Ladakh
Natural Resources
Looking at the physical resources specifically minerals Ladakh is blessed with abundant natural resources. It is also useful therefore from a military and geo-political perspective owing to its strategic location.
Tourism and Economy
The region has developed a strong tourism sector, as the bestowed landscapes of Ladakh attract travelers from all corners of the globe. Tourism is the main income-generating sector in the region, hence linking it well in the Indian economy framework.
Ladakh in Modern Geopolitics
Recent Developments
The Ladakh region is again in the spotlight of the world’s attention due to certain recent changes such as the rising military tensions between India and China.
Ladakh’s Strategic Location
These three regions have been divided based on the political boundaries of today’s states; geographically and culturally they are similar and are connected by the Himalayas The Strategic location of Ladakh between two nuclear powers threatening to attack each other that is Pakistan & China makes Ladakh a strategic military post for India.
Ladakh’s Disputed Status
Ladakh itself has been under the fire of both international territory claims since its formation of independent India in 1947. Even though Pakistan asserts territorial rights over the occupied part of Ladakh, the territory is internationally considered to be an integral part of India. This means that the Ladakhi future will continue to be subject to a struggle for its identity but for now interest in being a part of Indian Union territory will remain a reality.




